Android悬浮窗口的开发
1. 悬浮窗口的实现
使用悬浮窗口之前,要向用户申请权限
//在清单文件中定义权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW"/>
目标版本安卓6.0以上,还要在运行时申请权限
//在运行时申请权限
if (!Settings.canDrawOverlays(this)){
Intent floatPermission = new Intent(
Settings.ACTION_MANAGE_OVERLAY_PERMISSION, //不同于一般的权限,悬浮窗口权限是在独立的界面请求的
Uri.parse("package:" + getPackageName())); //带上自己的包名,打开自己软件的权限设置界面
startActivityForResult(floatPermission,REQ_FLOAT_PERMISSION); //打开设置界面
}
悬浮窗口的实现原理是利用WindowManager直接向屏幕添加视图
//获取WindowManager
WindowManager wm = (WindowManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
//适应安卓API的变化
int DEFAULT_WINDOW_TYPE;
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
DEFAULT_WINDOW_TYPE = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY; //最新安卓版本将应用的悬浮窗口独立出来了,使用专用的窗口类型
}else{
DEFAULT_WINDOW_TYPE = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_PHONE; //早期安卓版本,悬浮窗口使用PHONE窗口类型
}
//定义视图属性
lp = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
lp.flags = WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL //悬浮窗口不会占满屏幕,所以设置为视图外部不拦截点击事件
|WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_LAYOUT_IN_SCREEN //限制窗口显示在屏幕之类,按需设置
|WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE; //禁止悬浮窗口获取输入焦点,否则返回键之类的按键事件在别的应用程序中会失效,而且别的应用也不能输入文字
lp.format = PixelFormat.RGBA_8888; //设置颜色格式,支持透明
lp.gravity = Gravity.LEFT|Gravity.TOP; //重力左上角,方便调整位置和大小
lp.width = 320; //窗口宽320个像素
lp.height = 320; //窗口高320个像素
lp.x = 0; //距离屏幕左边0像素
lp.y = 0; //距离屏幕上方0像素
//这里的view可以是任意View类对象
//将视图属性赋给视图对象,并添加到屏幕上去
wm.addView(view, lp);
//使用结束,将视图从屏幕上移除
wm.removeView(view);
这里为了适应新版安卓,早期安卓使用TYPE_PHONE作为窗口类型,较新的安卓使用TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY作为窗口类型
2. 用户交互事件监听
像正常的视图对象一样,调用setOnClickListener之类的方法即可实现点击事件的监听
如果要监听窗口拖动的事件,最好在界面上布置一个透明Button,在其上面监听touch事件。实测的时候,直接在LinearLayout或TextView对象上面监听touch事件,只能收到touch_down回调,touch_move和touch_up事件都收不到。
3. 封装及使用
先来看看封装过后绘制出来的悬浮窗口长啥样:3
显示悬浮窗口
调整大小事件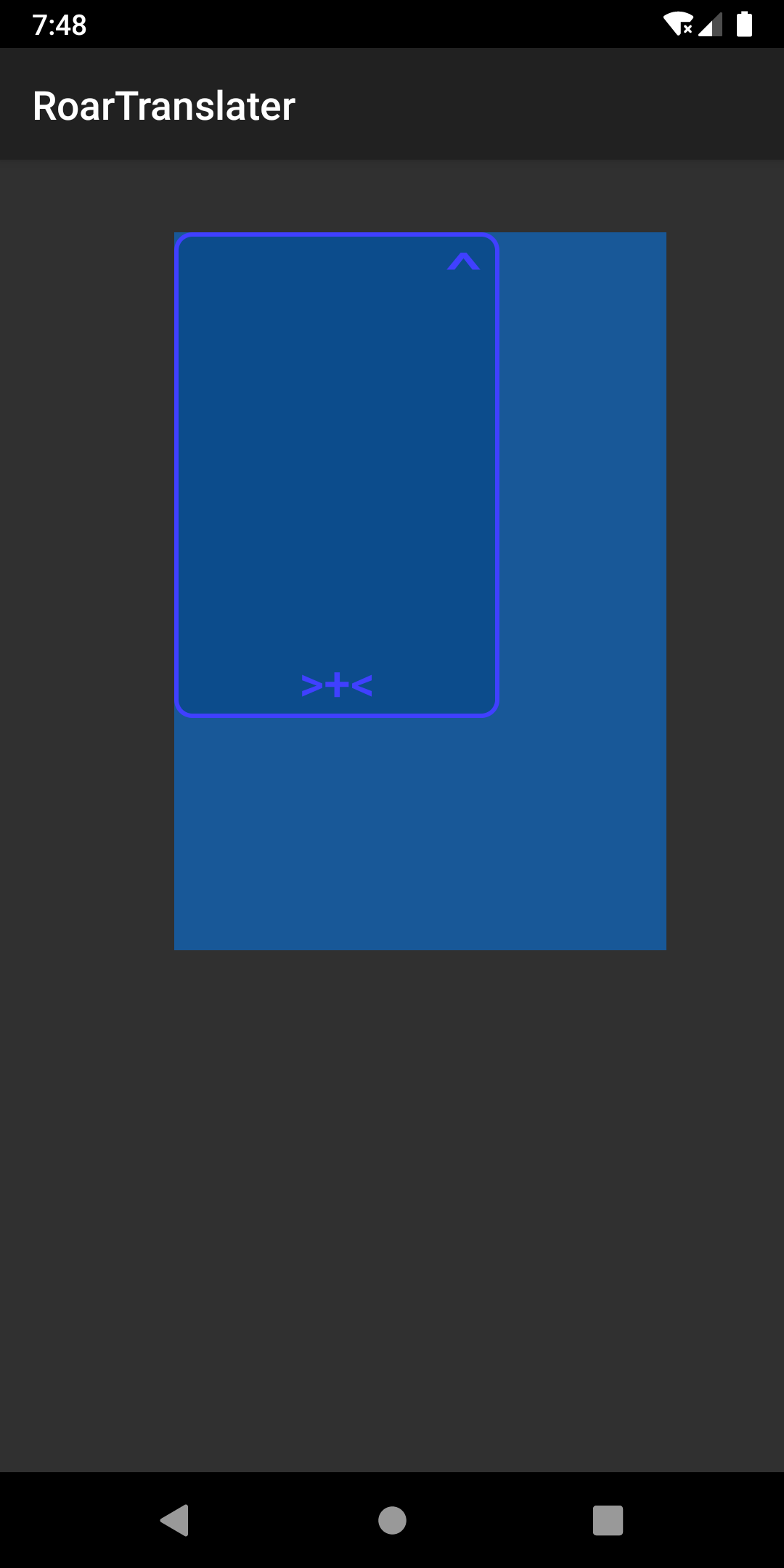
拖动事件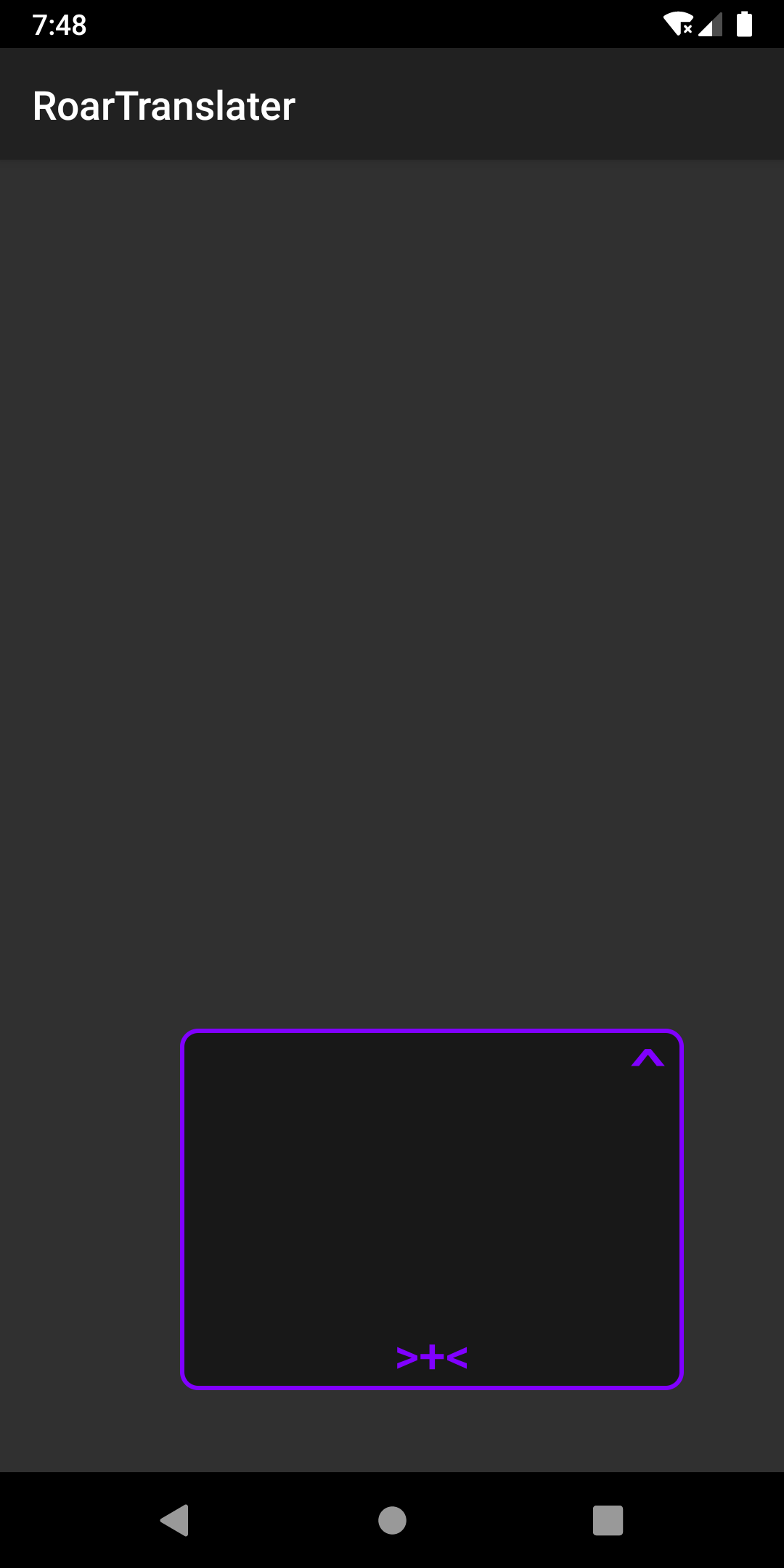
以下是封装的代码
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.PixelFormat;
import android.os.Build;
import android.util.DisplayMetrics;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.Gravity;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.widget.FrameLayout;
/*
* Manage the float windows easily
* Make the window looks like the window on Windows :p
* Created by Dreagonmon on 2017/1/15.
* 记得先申请悬浮窗权限!如果只想用APPLICATION层面的窗口,请修改DEFAULT_WINDOW_TYPE
*/
public class FloatWindow
{
public final int DEFAULT_WINDOW_TYPE;
public final int scrWidth;
public final int scrHeight;
public int minWidth;
public int maxWidth;
public int minHeight;
public int maxHeight;
private final WindowManager wm;
private final Context context;
private boolean isShowing = false;
private View view;//内容对象
private View window;//窗口对象
private WindowManager.LayoutParams lp;
private TouchListenerMove listenerMove = new TouchListenerMove();
private TouchListenerResize listenerResize = new TouchListenerResize();
private Runnable onPressAction;//点击事件
public FloatWindow(Context context)
{
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
DEFAULT_WINDOW_TYPE = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY;
}else{
DEFAULT_WINDOW_TYPE = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_PHONE;
}
this.wm = (WindowManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
this.context = context;
DisplayMetrics DM = new DisplayMetrics();
wm.getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(DM);
maxWidth = scrWidth = DM.widthPixels;
maxHeight = scrHeight = DM.heightPixels;
minWidth = 0;
minHeight = 0;
readyLp();
}
public FloatWindow(Context context,View view)
{
this(context);
this.setView(view);
}
private void readyLp()
{
lp = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
lp.type = DEFAULT_WINDOW_TYPE;//悬浮窗口类型,记得给予权限
//背景可点击,保持在屏幕内
lp.flags = WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL
|WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_LAYOUT_IN_SCREEN
|WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE;
lp.format = PixelFormat.RGBA_8888;//透明背景
lp.gravity = Gravity.LEFT|Gravity.TOP;//重力左上角,方便调整大小
lp.width = scrWidth;
lp.height = scrHeight;
lp.x = 0;
lp.y = 0;
}
/*内部元素操作类方法*/
/*
* setWindow()与setView()的区别:
* 一个会自动包裹进窗口内部,一个就是单纯的传入视图
* 当使用了setView的时候,getWindow()与getView()效果一样,
* 当使用了setWindow的时候,getWindow()返回窗口整体,getView()返回之前包裹的视图,*/
public View setWindow(int styleLayoutID,int containerID, View v)
{
/*主要内容容器
* 自定义layout布局,为styleLayoutID所指定的布局
* 最后自由添加内容的FrameLayout容器的ID为window_container*/
if (window == null||window.getId()!=styleLayoutID)
{
window = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(styleLayoutID,null);
}
FrameLayout container = (FrameLayout) window.findViewById(containerID);
v.setLayoutParams(new FrameLayout.LayoutParams(FrameLayout.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,FrameLayout.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT));
container.removeAllViews();
container.addView(v);
this.view = v;
return window;
}
public View getWindow()
{
return window;
}
public void setView(View view)
{
this.view = window = view;
}
public View getView()
{
return view;
}
public View getElementById(int ID)
{
return window.findViewById(ID);
}
public WindowManager.LayoutParams getLayoutParams()
{
return lp;
}
public void updateWindow()//配合取出的LayoutParams使用,记得改过lp之后更新窗口!
{
if (isShowing)
{
wm.updateViewLayout(window,lp);
}
}
public boolean isShowing()
{
return isShowing;
}
/*窗口设置类方法*/
/*
* 这几个事件最好是由窗口样式中的元素来设置,这样在更改内容View之后不需要再次设置
* OnPressAction仅作用于设置的MoveView,拖动距离不远的话算作点击,
* 该方法的调用在主线程,不要放置网络连接等操作,如果想取消点击事件,传入null即可
* Move和Resize被限制在屏幕之内,这是为了保证窗口的稳定
* 移动和改变大小事件推荐设置在Button上,TextView对touch事件的触发不完整
* 只有touch_down事件触发了回调*/
public void setMoveView(View v)
{
v.setOnTouchListener(listenerMove);
}
public void setMoveView(int ID)
{
View v = window.findViewById(ID);
if(v != null)
{
v.setOnTouchListener(listenerMove);
}
}
public void setResizeView(View v)
{
v.setOnTouchListener(listenerResize);
}
public void setResizeView(int ID)
{
View v = window.findViewById(ID);
if(v != null)
{
v.setOnTouchListener(listenerResize);
}
}
public void setOnPressAction(Runnable run)
{
onPressAction = run;
}
/*窗口行为类方法*/
/*记得先resize再move
* 为了保证所有按钮可用,这里的移动和调整大小的事件被限制为在屏幕之内*/
public void moveTo(int x,int y)
{
lp.x = x<0?0:(x+lp.width<=scrWidth?x:scrWidth-lp.width);
lp.y = y<0?0:(y+lp.height<=scrHeight?y:scrHeight-lp.height);
if (isShowing)
wm.updateViewLayout(window,lp);
}
public void moveBy(float xOffset,float yOffset)
{
lp.x =(int) (lp.x+xOffset<0?0:(lp.x+lp.width+xOffset<=scrWidth?lp.x+xOffset:scrWidth-lp.width));
lp.y =(int) (lp.y+yOffset<0?0:(lp.y+lp.height+yOffset<=scrHeight?lp.y+yOffset:scrHeight-lp.height));
if (isShowing)
wm.updateViewLayout(window,lp);
}
public void resizeTo(int width,int height)
{
lp.width = width<minWidth?minWidth:(width<=maxWidth-16?width:maxWidth);
lp.height = height<minHeight?minHeight:(height<=maxHeight-16?height:maxHeight);
if(isShowing)
wm.updateViewLayout(window,lp);
}
public void resizeBy(float xOffset,float yOffset)
{
lp.width =(int) (lp.width+xOffset<minWidth?minWidth:(lp.width+xOffset<=maxWidth?lp.width+xOffset:maxWidth));
lp.height =(int) (lp.height+yOffset<minHeight?minHeight:(lp.height+yOffset<=maxHeight?lp.height+yOffset:maxHeight));
if (isShowing)
wm.updateViewLayout(window,lp);
}
public void show()
{
if (!isShowing)
{
isShowing = true;
wm.addView(window, lp);
}
}
public void hide()
{
if (isShowing)
{
isShowing = false;
wm.removeView(window);
}
}
/*设计或许会用到的dp转px*/
public static int dp2px(Context context, float dipValue)
{
final float scale = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;
return (int)(dipValue * scale + 0.5f);
}
/*默认执行了移动和改变大小的点击事件后会移到最上层*/
class TouchListenerMove implements View.OnTouchListener
{
float lX,lY;
int startX,startY;
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View view, MotionEvent motionEvent) {
switch (motionEvent.getAction())
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
lX = motionEvent.getRawX();
lY = motionEvent.getRawY();
startX = lp.x;
startY = lp.y;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
moveBy(motionEvent.getRawX()-lX,motionEvent.getRawY()-lY);
lX = motionEvent.getRawX();
lY = motionEvent.getRawY();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
lX = lY = 0;
if (Math.abs(lp.x-startX)<5&&Math.abs(lp.y-startY)<5)
{
moveTo(startX,startY);
if (onPressAction!=null)
{
onPressAction.run();
}
}
//hide();
//show();
break;
}
return false;
}
}
class TouchListenerResize implements View.OnTouchListener
{
View tmpView;
WindowManager.LayoutParams tmpLp = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
float lX,lY;
private void resizeTmpView(float xOffset,float yOffset)
{
tmpLp.width =(int) (tmpLp.width+xOffset<minWidth?minWidth:(tmpLp.width+xOffset<=maxWidth?tmpLp.width+xOffset:maxWidth));
tmpLp.height =(int) (tmpLp.height+yOffset<minHeight?minHeight:(tmpLp.height+yOffset<=maxHeight?tmpLp.height+yOffset:maxHeight));
if (isShowing)
wm.updateViewLayout(tmpView,tmpLp);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View view, MotionEvent motionEvent) {
switch (motionEvent.getAction())
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
lX = motionEvent.getRawX();
lY = motionEvent.getRawY();
if (tmpView==null)
{
tmpView = new View(context);
tmpView.setBackgroundColor(Color.parseColor("#800080FF"));
}
tmpLp.x = lp.x;
tmpLp.y = lp.y;
tmpLp.width = lp.width;
tmpLp.height = lp.height;
tmpLp.type = lp.type;
tmpLp.flags = lp.flags;
tmpLp.format = lp.format;
tmpLp.gravity = lp.gravity;
wm.addView(tmpView,tmpLp);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
resizeTmpView(motionEvent.getRawX()-lX,motionEvent.getRawY()-lY);
lX = motionEvent.getRawX();
lY = motionEvent.getRawY();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
lX = lY = 0;
resizeTo(tmpLp.width,tmpLp.height);
wm.removeView(tmpView);
//hide();
//show();
break;
}
return false;
}
}
}
以下是使用的代码
FloatWindow fw = new FloatWindow(this);
fw.setWindow(R.layout.float_window_frame,R.id.window_container,new TextView(this));
fw.setMoveView(R.id.window_move);
fw.setResizeView(R.id.window_resize);
fw.minWidth = fw.minHeight = 320;
fw.resizeTo(480,640);
fw.moveTo(240,320);
fw.show();